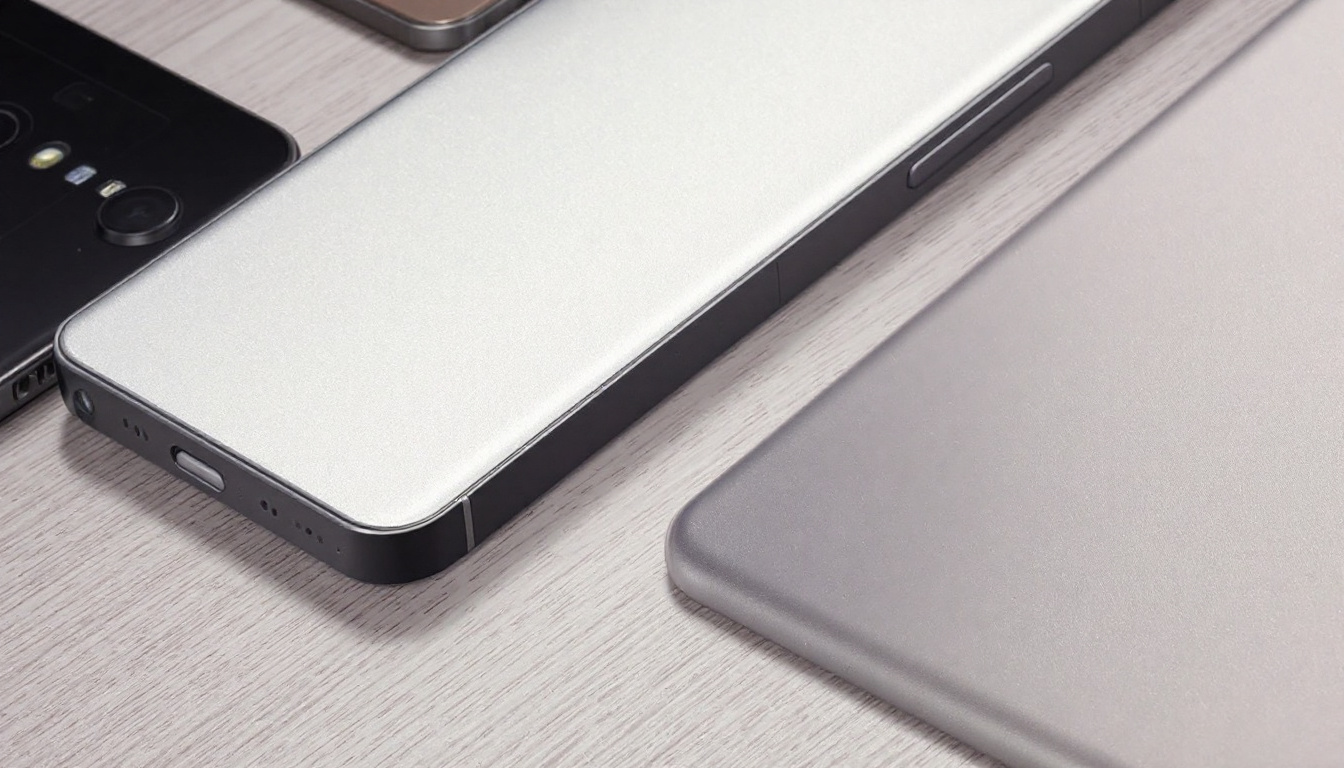
Material selection has become a main factor in evaluating new smartphones. Developers, IT professionals, and business users are giving close attention to build and durability when making device choices. The latest models feature a range of advanced materials, from reinforced glass to finely engineered metals and polymers “Compare Smartphone Build Quality & Durability”.
As devices become more integral to work and productivity, a strong and reliable build influences both day-to-day performance and long-term usability. Understanding the distinctions among competing smartphones helps professionals invest in hardware that will last and support business needs. This comparison provides clear insights into how the newest devices stand up to the demands of modern professional use.
Material Choices in Modern Smartphones
Modern smartphones use a selection of refined materials to achieve balance between strength, aesthetics, and weight. Manufacturers select metals, glass, ceramics, and polymers for their mechanical properties, usability, and visual appeal. Each material offers a unique set of advantages and drawbacks that directly impact performance and long-term satisfaction for business, IT, and engineering professionals.
Aluminum and Stainless Steel Frames (Compare Smartphone Quality Durability)
Aluminum is the preferred frame material for many flagship and mid-range smartphones. Its primary appeal lies in these traits:
- Lightweight: Aluminum reduces device weight without compromising strength.
- Corrosion Resistance: Keeps frames looking new after months of handling.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Devices resist bending and physical stress in daily use.
Stainless steel is common in select premium models. It carries a higher density, adding weight and a sense of sturdiness. The advantages include:
- Enhanced Rigidity: Devices with stainless steel feel more robust and endure greater forces.
- Polished Finish: Maintains a pristine appearance over time.
- Superior Scratch Resistance: Good for users who expect equipment to last.
Both aluminum and stainless steel allow manufacturers to design slim, rigid chassis while balancing heat dissipation and antenna performance. While aluminum is lighter and fosters easier signal transmission, stainless steel provides exceptional strength but can result in heavier devices.
To explore more about the shift towards robust metal frames in today’s phones, see the insights from TBS News on mobile phone durability.
Gorilla Glass, Ceramic, and Other Screen Materials (Compare Smartphone Quality Durability)
The display surface is one of the most sensitive parts of any device. Corning Gorilla Glass has become a standard for protecting these surfaces due to its high scratch resistance and impact strength. The latest iterations offer improved durability against drops and surface marks.
- Scratch Resistance: Minimizes everyday wear from keys, coins, and desks.
- Clarity: Preserves the original color and brightness of the display.
- Shatterproof Qualities: Each generation increases protection against cracks and chips.
Ceramic, used in limited high-end models, surpasses glass in hardness but can be more brittle when subjected to point impacts. Ceramic also maintains its appearance for longer, resisting micro-scratches and fading. The inclusion of sapphire glass in some specialty devices brings even stronger scratch resistance, but at increased cost and a higher tendency to shatter when dropped.
Manufacturers choose between these options based on their need for scratch resistance, visual clarity, and resilience to drops. Durability comes from pairing quality screen materials with reinforced frames and internal cushioning.

Polycarbonate and Alternative Plastics (Compare Smartphone Quality Durability)
While metals and glass often lead in flagship lines, polycarbonate and other plastics remain practical choices—especially in mid-range and business-focused devices.
- Impact Absorption: Unlike glass, plastic housings absorb shocks, reducing internal damage.
- Resilience to Cracks: Plastics bounce rather than break when dropped.
- Flexibility in Design: Allows for textured, matte, or glossy finishes, improving grip and reducing fingerprints.
Plastic does not dent or shatter as easily but can scratch and discolor with use. However, recent advancements in polymer science provide improved scratch and UV resistance, expanding plastic’s appeal for rugged or frequently handled business phones.
Discussions around premium feel often favor metal and glass, but the practical benefits of modern plastics cannot be ignored, especially for users seeking drop resistance and lower maintenance. For a breakdown on the enduring debate about the quality of plastic in phones, refer to the balanced view on Android Authority’s build materials comparison.
Employing these varying materials, manufacturers target different user priorities—be it lightweight mobility, high-end design, repairability, or resilience for busy environments. Selecting the right composition is key to balancing style, comfort, and lasting value for any professional.
Comparing Durability: Drop, Scratch, and Environmental Resistance
Today’s smartphones are built for more than style—they’re tools for professionals in demanding work settings. Their durability is often tested by real-world accidents, from drops to scratches and exposure to the elements. This section provides a balanced look at how the top models handle the kinds of abuse common in business, IT, and field work environments.
Drop Tests and Structural Integrity (Compare Smartphone Quality Durability)
Manufacturers frequently publicize drop test results to demonstrate the practicality of robust designs. Drop tests simulate everyday accidents, letting users measure which devices can survive frequent mishaps. The process usually involves dropping the phone onto different surfaces from standardized heights, with particular attention given to falls on corners, edges, and the screen.
- Metal frames (such as aluminum and stainless steel) add rigidity and can dissipate impact energy, reducing frame bends and chassis failures.
- Reinforced glass (like Gorilla Glass) provides some level of shock resistance but remains a common break point when landing face-down.
- Polycarbonate and durable plastics can absorb certain impacts better, flexing to diffuse shock but may not protect the screen as well as premium materials.
In comparative testing, as detailed in this phone drop test breakdown, many flagship devices withstand a typical back or side drop, but front-facing falls continue to cause the most damage. Field-ready business phones such as Samsung’s rugged models go a step further, meeting or exceeding military-grade standards in drop and structural integrity (Samsung’s durable smartphones).
Devices passing these tests decrease the risk of costly downtime or device replacements for enterprise users. Durability here signals a direct return on investment for IT departments managing large device fleets.
Scratch Resistance and Everyday Wear (Compare Smartphone Quality Durability)
Scratch resistance is critical for maintaining both function and professional appearance, especially with daily commutes, shared workspaces, and office environments. While hard glass types like Corning Gorilla Glass provide solid protection against everyday items (keys, coins, chargers), even the latest models can still show wear.
- Micro-scratches accumulate from brief contact with rough materials.
- Glass may resist deep scratches but not minor abrasions.
- Plastics scratch more easily but seldom shatter; ceramics offer enhanced scratch resistance but may crack under sharp impact.
Wear patterns can vary significantly. For example, recent reports highlight that some newer flagships, like the S24 Ultra, still attract fine marks in regular pockets (user feedback on scratch resistance). Confirming claims of “scratch-proof” is best done with standardized Mohs hardness testing. Most smartphones achieve ratings between 6 and 7 (out of 10) on this scale, meaning objects harder than this—such as quartz—can still scratch the screen (why Gorilla Glass still scratches).
Protective films and cases remain a smart investment for professionals who rely on the pristine appearance and resale value of their equipment.
Water, Dust, and Environmental Protection Ratings

Another key aspect for professional environments is resistance to environmental hazards. Smartphones now often feature certification for water and dust resistance, commonly expressed as IP (Ingress Protection) ratings.
- IP68 is typical for premium devices, indicating the phone can survive submersion in water to a certain depth for a defined period and is fully dust tight.
- Lower ratings (such as IP67 or IP65) also provide solid defense but with differing limits.
These protections are especially valuable for field use, construction, healthcare, and anywhere devices are routinely exposed to liquids or particulates. Not every phone is equal: while water resistance helps in brief accidental splashes, it does not imply invulnerability to prolonged submersion or high-pressure water (what do IP ratings really mean?).
Dust resistance ensures longevity in dry, windy, or industrial conditions. For businesses, confirming the IP rating is essential before deploying devices to field teams. This can help organizations reduce hardware failures and keep workflows uninterrupted—another cornerstone in effective device management.
To see additional smartphone comparison data, refer to internal resources such as the best rugged phone recommendations for options tailored to harsh environments.
Impact of Build Quality on Device Longevity and Repairability
Material choice determines not just how a smartphone looks and feels, but also how long it performs reliably and how easy it is to fix when problems arise. Structural integrity, fastening methods, and modular components affect whether a device can endure daily use while remaining serviceable over time. Companies are now evaluated on both how durable their phones are out of the box and how they support the ongoing usability through repair and upgrade options.
Repairability Scores and User Experience
Repairability is a measurable property of smartphones. Independent organizations and tech publications provide scores that reflect real-world repair scenarios. These scores factor in parts accessibility, required tools, and the presence of modular components.
For example, leaders like the Fairphone series consistently achieve high marks due to their straightforward disassembly and replaceable modules. In contrast, many flagship models from major brands use adhesive, proprietary screws, and fused assemblies, making even basic repairs complex for technicians and end users alike.
Smartphones with higher repairability scores not only reduce the total cost of ownership for businesses but also limit downtime. IT managers and enterprise users can prioritize models that are service-friendly, reducing both waste and support costs.
Readers can review up-to-date smartphone repairability scores to compare leading devices. Third-party rankings, such as the annual “Failing the Fix” report, also offer perspective on which brands prioritize repair access over compactness or design trends.
Device repairability contributes directly to productivity. Easily replaceable batteries, accessible displays, and standard fasteners all mean less time spent waiting on service calls and a faster return to work.
Sustainability and Upgradeability Considerations
Build quality is now linked closely to sustainability in the technology sector. Smartphones assembled from easily separated components can be repaired and recycled more efficiently. This approach keeps devices out of landfills and maximizes the lifespan of the original hardware.
- Modular designs: Models with removable back covers, standard batteries, and separable camera modules make upgrades and repairs straightforward.
- Material selection: Using screws and snap fits, instead of permanent adhesives, makes disassembly safer and less likely to damage parts.
Explore the intricate design and components on a green circuit board with capacitors and pathways.

Manufacturers who support longer-lasting devices also provide parts, updates, and repair manuals beyond the initial warranty period. This support is a growing concern for IT departments and sustainability-minded professionals who manage many devices.
Upgradeability, while rare in most mainstream phones, is gaining attention. For example, the Fairphone mentioned earlier allows users to swap cameras and batteries for newer versions, setting a standard for circular device use.
Material quality, assembly methods, and corporate repair policies work together to define how long a smartphone remains both useful and responsible. For scenarios that require ruggedness and field service—such as in logistics or engineering—reviewing manufacturer stance on repair and sustainability helps organizations avoid costly replacements. For further insights tailored to demanding environments, see recommendations for best rugged phones that prioritize both repairability and durability.
By considering these elements, professionals and IT managers can make decisions that support long-term value, user satisfaction, and responsible device use.
Material Quality Considerations for Professional and Enterprise Users
In professional settings, smartphones must meet higher standards than those expected from consumer devices. IT leaders, developers, and business managers require hardware that balances reliability, cost, design, and service life. Material quality is at the heart of device selection, influencing both daily usability and long-term return on investment.
Balancing Durability with Device Aesthetics

Business users often face a trade-off: choose the most robust material or prioritize a refined, premium look. Devices in the modern enterprise are expected to endure frequent handling, the occasional drop, and exposure to diverse environments—yet also convey professionalism during meetings or presentations.
- Metals like aluminum and stainless steel add rigidity and protect against flex and dents, while also giving an executive look and tactile feel.
- Reinforced glass enhances presentation but must offer sufficient impact and scratch resistance.
- Advanced plastics and polycarbonate, with the right texture and finish, provide impact absorption and can be styled for a modern, clean appearance.
Prioritizing aesthetic appeal does not have to come at the expense of practical strength. Many brands now blend materials and finishes, achieving devices that look sophisticated and maintain structural integrity. Surface treatments such as matte coatings or nano-textured glass further enable fingerprints resistance and better grip without sacrificing style. For an expanded checklist on material inspection, review smartphone quality control guidelines.
Evaluating Cost vs. Benefit for Business Deployment
When deploying smartphones across a team or organization, material choices directly affect both the upfront investment and the total cost of ownership. Aluminum and stainless steel frames, combined with durable glass, cost more at purchase but reduce the likelihood of frequent repairs or replacements.
Factors enterprise buyers should weigh:
- Initial device price versus potential repair/replacement cycles
- Service contracts and accident protection plans
- Likelihood of accidental damage in relevant work environments (offices, fieldwork, retail, etc.)
For roles exposed to greater risks—such as in logistics or on-site services—investing in ruggedized builds or models that use shock-absorbing polymers may lower long-term costs despite a higher initial price point.
A clear material evaluation, paired with knowledge of team needs and workplace risks, allows organizations to make cost-effective decisions. Technical reports, such as those in ScienceDirect’s analysis on smartphone durability, support the value of robust design in real-world use cases.
Recommended Strategies for Professional Buyers
Selecting smartphones for a professional environment requires more than comparing specifications. Professional buyers should develop a set of criteria that reflect usage patterns, workplace hazards, and budget limits.
Consider the following strategies:
- Develop a weighted checklist: Outline priorities such as drop resilience, repairability, and design. Assign relative importance based on user roles.
- Analyze historical device failure data: Use records from past hardware deployments to forecast likely wear points and compare repair vs. replacement costs.
- Request quality control documentation: Secure reports from vendors that detail construction materials, quality inspection processes, and environmental certifications. For a full inspection template, refer to this comprehensive smartphone inspection checklist.
During selection, it’s also important to evaluate how device build quality will support digital work. For those considering deployment of professional digital tools, the guide on top digital products IT professionals should sell in 2025 provides insight on aligning device capabilities with workplace needs.
Procurement teams should routinely review market updates and material trends to stay ahead of durability and cost developments. Establishing clear selection frameworks leads to a more resilient workforce and safeguards technology investments.
Conclusion
Material quality shapes every aspect of smartphone performance in demanding environments. The right choice allows professionals in IT, development, and business to maintain productivity while minimizing long-term costs and device downtime. Build strength, resistance to accidents, and repair access offer measurable value, especially when choosing technology for teams and enterprise use.
Selecting devices based on proven durability and practical repairability supports both efficiency and a better return on technology investments. For work settings that require robust hardware, reference guides like the best rugged phone recommendations help match users with the right device for their needs.
Thoughtful evaluation of material quality—beyond surface appeal—ensures each device meets modern professional standards. Review new releases with a focus on long-term reliability, and continue exploring site resources for advanced selection strategies and ongoing updates.